Astroshop is a great way of testing and running a demo scenario that offers with a large spectrum of technologies, services and a realistic problem scenario of running a real shop in serverless or Kubernetes infrastructure.
Besides, Astroshop being a great way to demo and test observability platforms such as Dynatrace and to run problem scenarios on demand, its also a bit cumbersome to deploy it for testing purposes. Imagine that you are a local developer that just needs to quickly run a test for a new feature using OTel traces and spans. Deploying Astroshop or any other scenario always comes with some cost, effort and with some unpredictability in terms of how the underlying infrastructure reacts. Sure, for integration tests you definitely need that unexpected infrastructure behavior, but for doing some functional tests, its fully sufficient to run a simulated stream of OTel data against your observability platform.
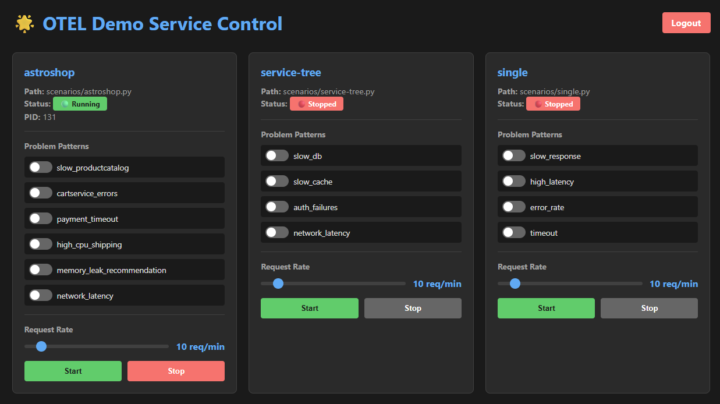
And thats where my ‘vibe-coded’ OTel demo service comes into play, as it gives a local developer direct control over a scenario. The OTel demo service offers a convenient web interface for starting various scenarios, from simulating a simple scenario, over simulating a more complex service tree over to a complete simulated Astroshop scenario.
The OTel demo service also allows you to toggle problem scenarios on and off in order to test an observability frameworks way of alerting on specific scenarios.
AI-generated OTel test scenarios
The complete scenarios are AI-generated. They use realistic service names, service latencies and error rates and also do connect the services in a realistic way.
Using AI to automatically generate such scenarios is the ideal use of generative AI, as each coding model, like GitHub CoPilot or Claude Caude does exactly know the full and detailed documentation and architecture of Astroshop and will therefore generate a scenario with realistic service names, span connections.
If we would like to try to replicate the same result by manually connecting each Otel span into a realistic trace, it would be an extremely cumbersome work of several hours at least.
Using GitHub CoPilot to fully generate my Open Telemetry trace scenarios not only saved me days of work but also does not produce any AI costs after the scenario code was generated. Even better, it saves me costs when running the scenario on a simplistic node instead of fully deploying the Astroshop workload itself.
After configuring a OTel receiver such as Dynatrace, you can see the result of the simulators generated Open Telemetry traces and spans directly within your observability solution.
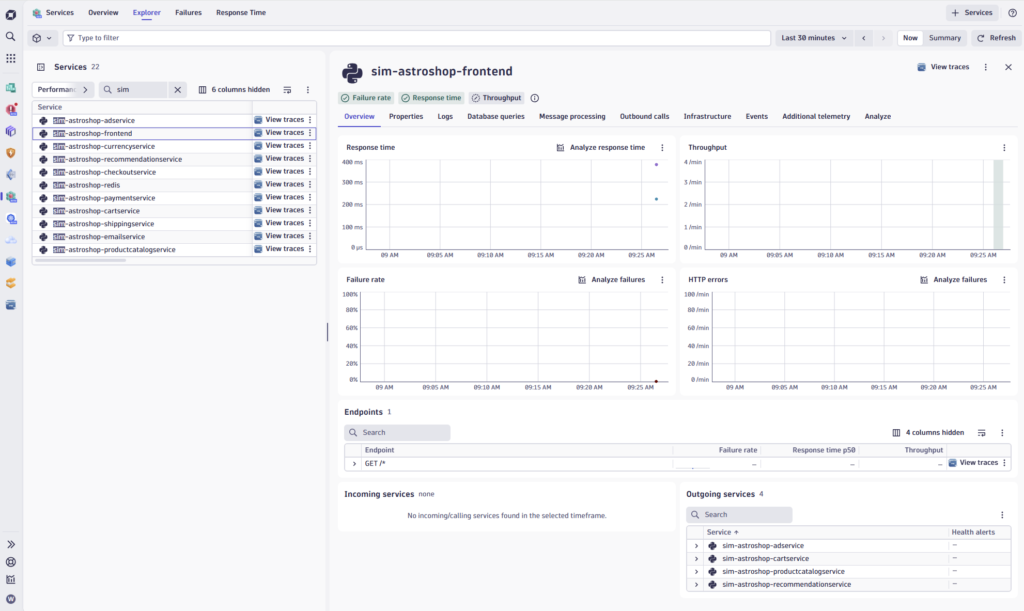
You can easily try to extend the OTel scenarios by just instructing GitHub CoPilot to implement another scenario replicating a system you would like to simulate, lets say a running WordPress instance hosted in AWS cloud.
GitHub CoPilot or Claude Code will do the rest for you, using its huge community knowledge of how such a scenario must look like, what services typically are involved and what typical behavior characteristics look like for that demanded scenario.
Summary
Overall, this tiny OTel trace simulator project does confirms my long standing opinion that generative AI models are brilliant in helping to test software systems and to easen the task of every software tester by proving realistic test cases and scenarios.
Download, run and use my Astroshop OpenTelemetry demo service from GitHub.